Physical Layer Security Analysis of Hybrid MIMO Technology.
In this work, the authors analyze and quantify the security performance of Hybrid MIMO, which was originally proposed by the preceding work titled “Hybrid MIMO: A New Transmission Method For Simultaneously Achieving Spatial Multiplexing and Diversity Gains in MIMO Systems”.
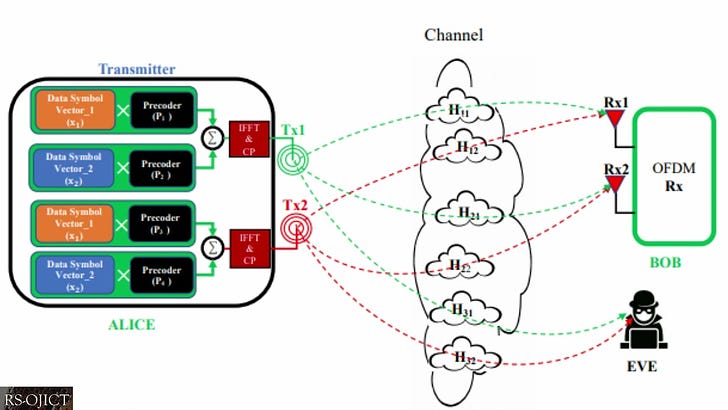
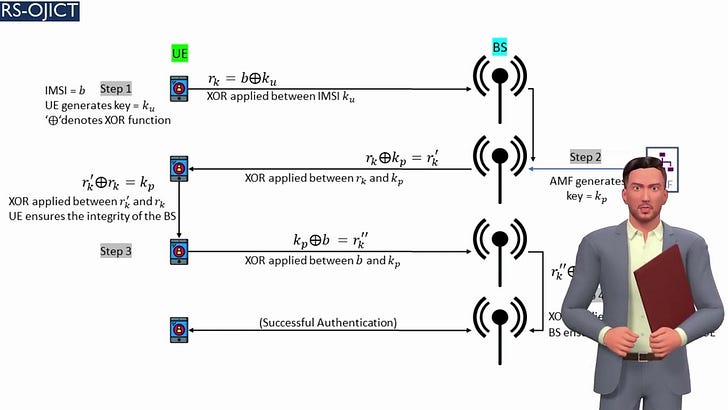
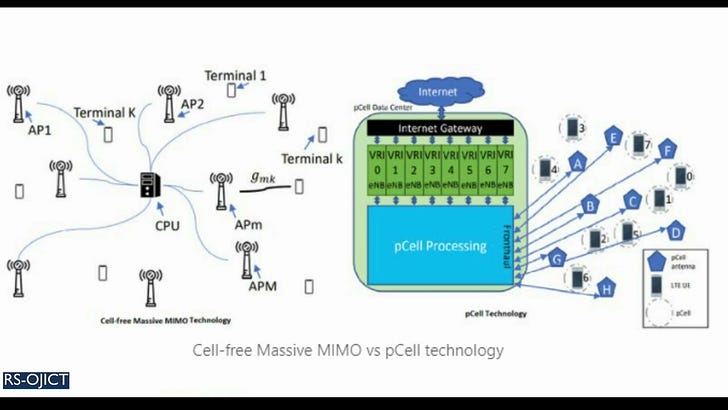
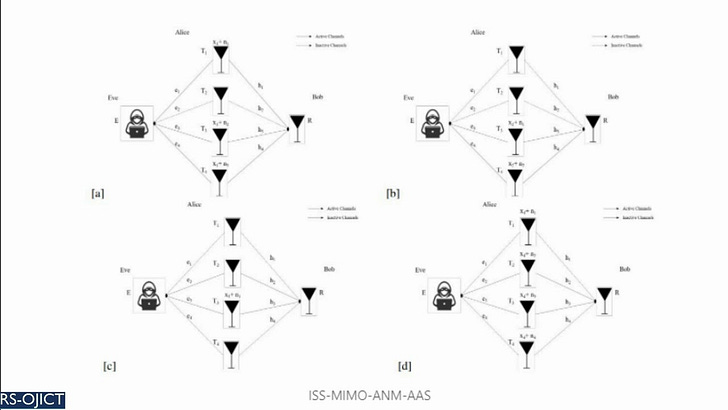
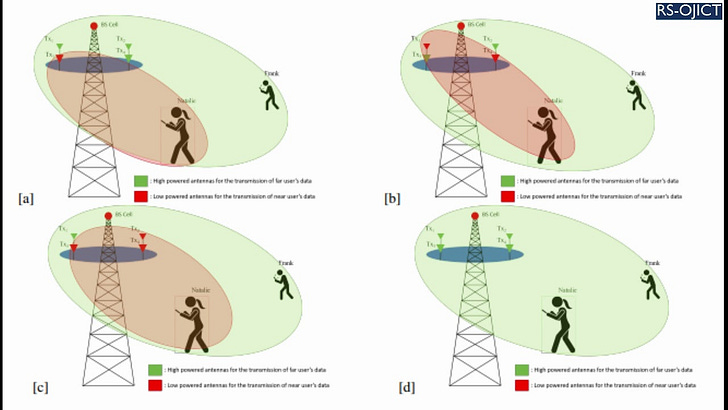
Summary: MIMO is a key enabling technology in the currently emerging 5G systems and future 6G-plus paradigms, such as heterogeneous networks, millimeter-wave networks, vehicular sensor networks, among others. The highly desired properties of MIMO such as its ability to support high data rates, improving energy and spectral efficiency, as well as overcoming the effects of shadowing and fading have made it increasingly attractive to the wireless communications industry. Nevertheless, a practical secure MIMO model with the required security levels to guarantee user information protection has still not been realized by the industry. In this work, we analyze and quantify the security performance of hybrid MIMO, which was originally proposed by the preceding work titled “Hybrid MIMO: A New Transmission Method For Simultaneously Achieving Spatial Multiplexing and Diversity Gains in MIMO Systems”. In the proposed method, special signal interference-canceling matrices, which are calculated based on the channel’s variations and randomness between the user and receiver, are superimposed with user data at the physical layer level before being transmitted to the receiver. The conducted performance analysis in this study indicates that the signal interference-canceling matrices provide absolute security (zero information leakage) against both internal and external eavesdroppers. Moreover, the new MIMO technique eliminates the need for any processing at the receiver, where users directly receive their intended signals, consequently lowering complexity and power consumption at the receiver. These are highly desirable properties for the future internet of things (IoT) devices as well as 6G and beyond technologies.
PDF: https://rs-ojict.pubpub.org/pub/1v7f9...
CODES: https://researcherstore.com/product/h...
Improve your professional and technical skills at: https://researcherstore.com/




Physical Layer Security Analysis of Hybrid MIMO Technology